Remembering John Brown
From RHESSI Wiki
Contents |
John C Brown (1947-2019)
John Brown passed away unexpectedly on 16 November 2019, a great sadness to all who knew him and a huge loss particularly to the Glasgow Astronomy and Astrophysics group. His many contributions to solar physics were highly influential and we were prompted to think back over some of the big themes of his research career. In this nugget we look at one of those big themes, inverse problems in astrophysics. This particular topic spans the whole of John's research career and combines a technical side with a more philosophical approach to the character of data and the limits on what one can deduce from them.
Brown(1971)
John's first paper was published in 1971. As of 22 November 2019, ADS says it has been cited 889 times. It introduced several ideas that became key to the study of flares and their X-radiation. A previous nugget dealt with the thick target model. Another new idea was the possibility of "inverting" observed X-ray spectra to deduce the energy distribution of the emitting electrons. Electrons are accelerated to 10s of keV energy in the flare. The hard X-rays they emit via bremsstrahlung yield information on their number and energies.
The bremsstrahlung cross-section dσ/dε gives the probability that an electron of energy E will emit a photon of energy ε. At any instant, the flux at Earth is I(ε):
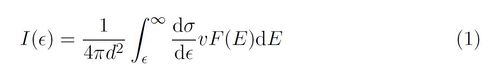
Here d = 1 AU, v is the speed of an electron of energy E and
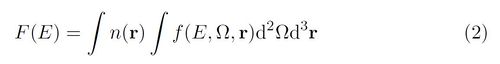
i.e., the angle-averaged electron distribution f weighted by ambient density n and integrated through the whole of the source region. In the limiting, thick or thin target cases, F(E) can be simply related to the flux of electrons being injected to the X-ray emission region - information that should be intimately related to the behaviour and physical character of the energy release process.
How do we use Equation (1) and the observed spectrum to learn about the fast electron population F? One approach is to assume a parametric form for F(E), e.g. the power-law AE-δ and adjust the parameters (in this example, δ and A) to obtain the best fit to I(ε). An alternative approach regards (1) as an integral equation and attempts to solve for the unknown F(E). John employed the Born approximation bremsstrahlung cross-section due to Bethe and Heitler, in its non-relativistic limit, and showed that (1) reduced to an instance of Abel's integral equation. Since this equation has a known, analytical solution, this opens up the possibility of deriving the form of F(E) directly, non-parametrically from the form of I(ε). What a discovery!
If we use more precise expressions for the cross-section the analytical solution of Abel's integral equation is no longer applicable but a numerical (matrix) process can still be constructed, deducing a vector of values F = (F1,F2,F3...FM) from a histogram of values I = (I1, I2,...,IL).
In practice this analytical solution is not so easy to use. It involves the first and second derivatives of I(ε), difficult to obtain from noisy data. Also the scintillators used for hard X-ray spectroscopy in the 1970s, NaI(Tl) etc., had a typical energy resolution δε/ε of about 10% or worse, inadequate for implementation of this approach. The possibility might be realisable with other sorts of X-ray spectrometer, however.
Ill-conditioned problems
The relationship of (1) may be approximated as
where the matrix M follows from the details of the cross-section and whatever precise discretisation scheme is used to approximate the integral as a finite sum. We have also added the vector ξ of noise values, recognising the realities of photon count statistics and instrumental imperfections.
In the absence of noise Eq. (3) can be solved:
One might hope that a very fine instrument of enormous collecting area might make the errors ξ small enough that this straightforward inversion will give fairly good results. Such optimism proves naïve. One finds that even tiny levels of noise are greatly amplified in implementing Eq. (4) so that the results fluctuate wildly, even sometimes taking negative values: the problem is ill-conditioned. The condition number of the matrix M quantifies the magnitude of this data sensitivity.
Inverse problems of the form of Eq. (4) turn up in many places in astrophysics. In flare physics we find another example in the deduction of the temperature distribution of emission measure from measurements of the intensity of a set of spectrum lines. These problems were highlighted by John and Ian Craig in a couple of papers in 1976, one of them in Nature bearing the provocative title, Why measure astrophysical X-ray spectra?. The key point is a brutal one, embodying John's characteristic iconoclastic scepticism: the nature of the inversion process, rather than the quality of the instrument, may limit what can be deduced from observed spectra. Unsurprisingly these contributions drew some robust responses.
Regularisation
In 1986 Ian Craig and John published their monograph, Inverse Problems in Astrophysics. This classic text reviewed the character of inverse problems met in several domains of astrophysics, underlined the ill-posed character of many of these, and advocated the use of regularisation approaches to inversion in the presence of noise. In the presence of noise one cannot use the classical, analytical solutions of integral equation theory. One is forced to adopt a statistical approach, constructing an estimator for the desired quantity. Instead of aiming for an exact solution one introduces a (Lagrange multiplier) parameter λ and finds an extreme value of
![]() where we have introduced a function Φ that encodes some desired property of the solution: that it should be maximally 'smooth', that its norm be minimised, that it conforms as closely as possible with some other knowledge one has, etc.. The situation is illustrated in this picture, in which: the blue point represents exact fit to data; the blue curves are of constant χ2; the red point represents the unconstrained maximum of ^Phi;; and each red curve shows constant Φ. λ increases upwards along the dashed curve, so that it parametrises the degree of compromise between exact data fit and prior assumptions about the solution (e.g. maximally 'smooth').
where we have introduced a function Φ that encodes some desired property of the solution: that it should be maximally 'smooth', that its norm be minimised, that it conforms as closely as possible with some other knowledge one has, etc.. The situation is illustrated in this picture, in which: the blue point represents exact fit to data; the blue curves are of constant χ2; the red point represents the unconstrained maximum of ^Phi;; and each red curve shows constant Φ. λ increases upwards along the dashed curve, so that it parametrises the degree of compromise between exact data fit and prior assumptions about the solution (e.g. maximally 'smooth').
Several strategies are available, each with its pros and cons for choosing the form of Φ and then the optimal value of λ.
Examples of these techniques at work are found in the inversion of the synchrotron radiation spectrum of the Crab nebula and in image deconvolution for the HXIS instrument on SMM.
RHESSI
Although inversion of the hard X-ray spectrum was a key feature of John's very first paper it only became practical when germanium detectors, with their much higher spectral resolution, were placed in space. The HIREGS balloon-borne experiment yielded data that could be analysed in this way but the potential of
The launch of RHESSI